1. Hard water and soft water: the definition is revealed
In the industrial field, the classification of water is often based on the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions it contains, which directly determines whether the water is hard water or soft water. Essentially, hard water refers to water that contains more soluble calcium and magnesium compounds, while soft water is water that contains no or less soluble calcium and magnesium compounds. This classification has clear quantitative indicators, and "hardness" is usually used to measure the content of calcium and magnesium ions in water. There are many ways to express the unit of hardness. The most commonly used is the German degree (°dH), 1 German degree is equivalent to 10 mg of calcium oxide (CaO) per liter of water. In industrial standards, water with a hardness of less than 8 German degrees is generally considered soft water; and water with a hardness of more than 8 German degrees is classified as hard water. In order to more accurately measure the hardness of water, the content of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is usually used as a standard, with the unit being milligrams per liter (mg/L). However, there may be some subtle differences in the specific classification standards for hard water in different countries and regions, but in general, they are defined around the content of calcium and magnesium ions in water.
For example, when we test a water sample, if the calcium and magnesium ions in it are converted into calcium oxide and the content per liter of water is less than 80 mg, then it is soft water; on the contrary, if it exceeds 80 mg, it belongs to the category of hard water. There is also a more detailed classification, which calls the hardness between 8-17 German degrees as moderate hard water, and the hardness above 17 German degrees as highly hard water. The total hardness of water cannot exceed 450 mg. This quantitative distinction standard provides an important basis for the precise control of water quality in industrial production processes. Different industries can strictly screen and process the hardness of water according to their own production needs.
2. Detection of "hard and soft" water in life
In daily life, we can also use some simple methods to preliminarily judge whether the water is hard water or soft water. These methods are not only interesting, but also allow us to have a more intuitive feeling of hard water and soft water. Soap water method: This is the most commonly used identification method. Take equal amounts of two water samples, pour them into two clean containers respectively, then add equal amounts of soapy water to them, stir thoroughly and observe the phenomenon. If a large amount of rich, delicate foam appears on the water surface, and there is almost no scum, then this is soft water.
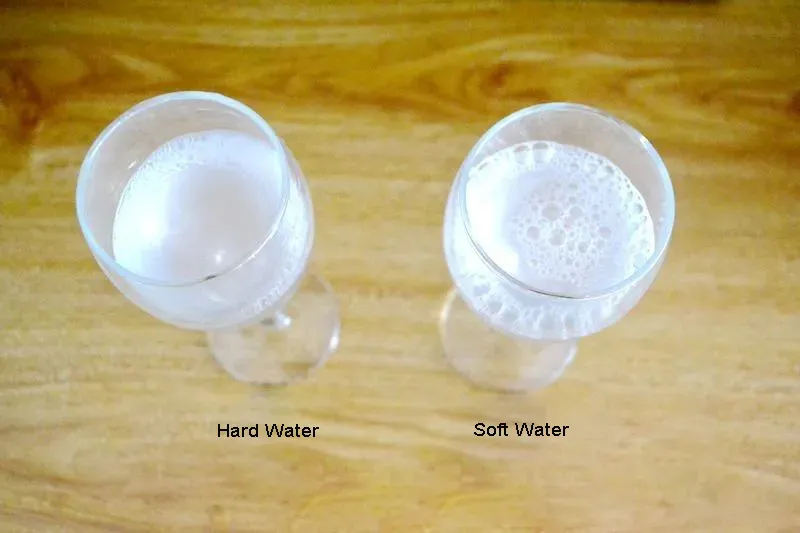

On the contrary, if there is little foam on the water surface, but a lot of scum is produced, then it is undoubtedly hard water. The principle behind this is that sodium stearate, the main component of soap, will ionize into stearate ions and sodium ions in water. A large amount of calcium ions and magnesium ions in hard water will combine with stearate ions to form water-insoluble calcium stearate and magnesium stearate precipitation, which will lead to the appearance of scum and make it difficult to produce foam; while there are very few or even no calcium and magnesium ions in soft water, so it can produce rich foam with soapy water.
Heating to see scale method: Pour the two water samples into a clean kettle or beaker respectively and heat them. After a period of time, carefully observe the changes in the inner wall of the container. If a large amount of white, hard scale is left on the container wall, it means that this water sample is hard water. Because the soluble calcium and magnesium compounds in hard water will undergo chemical reactions during the heating process and transform into insoluble calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide and other substances. These substances adhere to the container wall and form scale; soft water will hardly produce scale after heating, and the container wall remains relatively clean.
Evaporation and residue method: Take a clean, dry glass and drop equal amounts of two water samples at different locations. Place the glass in a safe place and wait for the water to evaporate naturally. When the water evaporates completely, observe the situation on the glass. If there are more white residues, it means that the water sample is hard water, and these residues are the calcium and magnesium compounds in the hard water; after the soft water droplets evaporate, there is almost no obvious residue on the glass, or only a very small amount of traces.
3. "Trouble" of hard water in industry
In industrial production, the existence of hard water is like a hidden "time bomb", which brings many troubles and hazards to the production process. "Fatal killer" of boilers: In industrial scenarios with boilers as core equipment, such as thermal power generation, steam heating and other industries, hard water is a huge threat. When hard water enters the boiler and is heated, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water will gradually form insoluble precipitations such as calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide as the temperature rises, which is what we commonly call scale. These scales will adhere tightly to the heating surface of the boiler, such as the inner wall of the furnace tube and the drum. The thermal conductivity of scale is extremely poor, and its thermal conductivity coefficient is only a few hundredths of that of steel. This is like adding a thick insulation layer between the heating surface of the boiler and the high-temperature flame, making it difficult for heat to be effectively transferred from the heating surface to the water. In order to achieve the predetermined steam output and pressure, the boiler has to increase the amount of fuel input, resulting in a large waste of energy. Data show that for every 1 mm increase in the thickness of the scale in the boiler, the fuel consumption will increase by 3% - 5%. Not only that, scale can also cause local overheating of the boiler, reduce the strength of the metal material, and then cause serious safety accidents such as bulging, deformation and even explosion. In some small factories, due to poor management of boiler water quality, boiler explosions caused by hard water scaling occur from time to time, causing huge casualties and property losses. The "blocking culprit" of the cooling system: In the chemical, metallurgical, and mechanical manufacturing industries, the cooling system plays a vital role. It can ensure that the equipment maintains a suitable temperature during operation and prevent the equipment from being damaged by overheating. However, hard water can cause serious blockage problems in the cooling system. When hard water circulates in the cooling pipe, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water will gradually precipitate, forming scale and adhering to the inner wall of the pipe. As time goes by, the scale will continue to accumulate, causing the inner diameter of the pipe to gradually decrease, and the water flow resistance to increase, resulting in a significant decrease in cooling efficiency. In severe cases, the scale will even completely block the pipe, making the cooling system unable to work normally, and forcing the entire production process to be interrupted. A chemical company once used hard water in the cooling system and did not soften it in time, resulting in serious scaling of the pipe. During a production peak, the cooling system suddenly paralyzed, and a large amount of reaction heat could not be discharged in time, causing drastic fluctuations in the production equipment and causing millions of economic losses.
"Quality Nemesis" of Textile Printing and Dyeing: In the textile printing and dyeing industry, water is an indispensable and important raw material. From fabric pre-treatment, dyeing to finishing, every link cannot do without water. However, the presence of hard water will have a great negative impact on the quality of textiles. During the dyeing process, the calcium and magnesium ions in hard water will react with the dye to form an insoluble metal complex, which will cause the dye to be unable to adhere evenly to the fabric, resulting in uneven dyeing and dull color. These problems not only affect the appearance of textiles, but also reduce the grade and market competitiveness of the products. In addition, hard water will also form scale precipitation on the surface of the fabric, making the fabric feel rough and reducing the comfort of wearing. For some high-end textiles, such as silk and cashmere products, the harm of hard water is more obvious, and the slightest carelessness will cause the entire batch of products to be scrapped.
"Health hazards" of food processing: In the food processing industry, the quality of water is directly related to food safety and consumer health. During food processing, hard water may introduce too much calcium, magnesium and other minerals. Excessive accumulation of these minerals in food will not only affect the taste and flavor of the food, but also pose a potential threat to human health. For example, when brewing beer, if hard water is used, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water will react with the enzymes in the malt, affecting the activity of the enzymes, resulting in abnormal fermentation, poor taste of beer, and shortened shelf life. In dairy processing, hard water may coagulate the protein in milk, affecting the quality and stability of dairy products. Long-term drinking of foods made with hard water containing excessive minerals may also increase the risk of diseases such as stones. It can be seen that the harm of hard water in industrial production is multifaceted. It not only affects production efficiency and product quality, but also increases production costs and safety risks. Therefore, for industrial enterprises, taking effective hard water treatment measures to convert hard water into soft water is the key to ensuring normal production, improving product quality, reducing costs and ensuring safety.
4. Soft water: "ideal water" for industrial production
In sharp contrast to hard water, soft water can be called the "ideal water" in industrial production and plays an indispensable role in many industries. In the electronic power industry, the requirements for water quality have almost reached the extreme. Whether it is chip manufacturing, circuit board production, or cleaning and assembly of electronic equipment, soft water is an indispensable key element. In the chip manufacturing process, even extremely trace amounts of impurities such as calcium and magnesium ions may cause the chip circuit to short-circuit, performance degradation, or even scrap. For example, when producing high-end smartphone chips, the ultrapure water used is actually deeply treated soft water with a hardness of almost zero, ensuring the high precision and stability of chip manufacturing. In the power industry, power generation equipment such as steam turbines and generators need to use soft water as a cooling medium and boiler feed water. Soft water can effectively avoid scaling inside the equipment, ensure the efficient operation of the equipment, reduce maintenance costs, and improve power generation efficiency. A large thermal power plant uses advanced softening water equipment to soften raw water for boiler water replenishment, which increases the thermal efficiency of the boiler by 5% and saves millions of yuan in fuel costs each year. The pharmaceutical industry also has a strict dependence on soft water. From drug research and development, production to quality inspection, every link is inseparable from the participation of soft water. In the process of drug production, soft water, as a solvent, cleaning agent and reaction medium, directly affects the quality and safety of drugs. If hard water is used, impurities in the water may react chemically with the ingredients of the drug, change the properties and efficacy of the drug, and even produce harmful substances. For example, in the production of injections, softened water that meets the pharmacopoeia standards must be used to ensure the purity and sterility of the drug. In the cleaning process of pharmaceutical equipment, soft water can also effectively remove dirt and residual drugs on the surface of the equipment, prevent cross contamination, and ensure the normal operation of the equipment. Many production processes in the chemical industry are also inseparable from the support of soft water. In chemical reactions, soft water can be used as an ideal reaction medium to ensure the smooth progress of the reaction and the stability of the product quality. For example, in the synthesis process of fine chemical products, the use of soft water can avoid the influence of impurities in the water on the reaction catalyst and improve the selectivity and yield of the reaction. In the separation and purification process of chemical products, soft water is also often used for washing and extraction, which can effectively remove impurities in the product and improve the purity of the product. In addition, the use of soft water in cooling systems, steam boilers and other equipment in chemical production can prevent scaling and corrosion, extend the service life of the equipment and reduce production costs. In addition to the above industries, soft water is also widely used in food and beverage, textile printing and dyeing, papermaking and other industries. In the food and beverage industry, soft water is used for processes such as cleaning, blending, and cooking of raw materials to ensure the taste and quality of the product and avoid odor and precipitation problems caused by hard water. In the textile printing and dyeing industry, soft water can be used in the dyeing and rinsing of fabrics to avoid the combination of calcium and magnesium ions in hard water with dyes, affecting the dyeing effect and the color brightness of the fabric. In the papermaking industry, the use of soft water can prevent equipment scaling, improve the quality and production efficiency of paper, and reduce paper defects and production accidents caused by water quality problems.
5. The magic of "softening" hard water
Facing the many problems caused by hard water in industrial production, scientists and engineers have developed a series of effective hard water softening methods. These methods are like magic, which make hard water "renovate" and become a high-quality water source that meets the needs of industrial production. Precipitation method: Precipitation with chemicals Precipitation method is a more traditional and commonly used hard water softening method. Its principle is to add specific chemical agents, such as lime (Ca (OH)₂) and soda ash (Na₂CO₃), to hard water to make the calcium and magnesium ions in the water react chemically with the agents to form insoluble precipitates, which are then separated from the water. Taking hard water containing calcium bicarbonate (Ca (HCO₃)₂) and magnesium bicarbonate (Mg (HCO₃)₂) as an example, after adding lime, the following reaction will occur: Ca (HCO₃)₂ + Ca (OH)₂ = 2CaCO₃↓ + 2H₂OMg (HCO₃)₂ + 2Ca (OH)₂ = Mg (OH)₂↓ + 2CaCO₃↓ + 2H₂OThe calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) and magnesium hydroxide (Mg (OH)₂) precipitates generated by the reaction can be removed by filtration, thereby reducing the hardness of the water. The advantages of the precipitation method are relatively low cost, simple equipment, easy operation, and certain advantages for treating large flows of hard water. The precipitation method has been widely used in some industrial fields that do not require particularly high water quality, such as cooling water in steel plants and production water in cement plants. However, the precipitation method also has obvious limitations. It can only remove some calcium and magnesium ions in the water. For some calcium and magnesium ions in the form of sulfate and chloride, the precipitation method is not ideal and it is difficult to reduce the hardness of water to a lower level. In addition, the precipitation method will produce a large amount of chemical sludge. The treatment and disposal of these sludges require additional costs and technologies. If they are not handled properly, they may also cause secondary pollution to the environment.
Ion exchange method: The magical ion replacement ion exchange method is one of the most widely used hard water softening methods in industry. Its core principle is to use the ion exchange capacity of ion exchange resin to replace calcium and magnesium ions in water with sodium ions (Na⁺) or hydrogen ions (H⁺) on the resin, so as to achieve the purpose of softening water. Ion exchange resin is a high molecular polymer with a network structure, which contains a large number of exchangeable ion groups. When hard water passes through an exchange column filled with ion exchange resin, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water will undergo the following exchange reaction with the sodium ions on the resin: 2R - Na + Ca²⁺ = R₂ - Ca + 2Na⁺2R - Na + Mg²⁺ = R₂ - Mg + 2Na⁺ (where R represents ion exchange resin) After ion exchange, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water are adsorbed on the resin, while the sodium ions on the resin enter the water, significantly reducing the hardness of the water. When the calcium and magnesium ions adsorbed by the ion exchange resin reach a certain level, the exchange capacity of the resin will decrease, and the resin needs to be regenerated. The regeneration process usually uses concentrated brine (such as NaCl solution) to rinse the resin so that the calcium and magnesium ions on the resin are replaced by sodium ions, thereby restoring the exchange capacity of the resin. The advantages of the ion exchange method are very prominent. Its softening effect is stable and reliable, and it can reduce the hardness of water to a level close to zero, meeting the needs of various industrial productions with extremely high water quality requirements, such as electronic chip manufacturing, pharmaceuticals and other industries. In addition, the ion exchange method has a small equipment footprint, a high degree of automation in operation, and a relatively low operating cost. However, the ion exchange method is not perfect. The price of ion exchange resins is relatively high, and the initial equipment investment is large. Moreover, a large amount of salt-containing wastewater will be generated during the regeneration process. If it is not properly treated, it will pollute the environment.
Reverse osmosis: The miracle of precision filtration
Reverse osmosis is an advanced technology that uses the selective permeability of a semipermeable membrane to separate the solute and solvent in the water under pressure to achieve the purpose of softening water. A semipermeable membrane is a special membrane that only allows water molecules to pass through, but does not allow solute molecules (such as calcium, magnesium ions, etc.) to pass through. When hard water passes through a semipermeable membrane under a pressure higher than its osmotic pressure, water molecules will pass through the semipermeable membrane to the other side, while impurities such as calcium and magnesium ions in the water are retained on the raw water side of the semipermeable membrane, thereby achieving water softening and purification. Reverse osmosis has many significant advantages. It has an excellent softening effect and can effectively remove various ions, microorganisms, organic matter and other impurities in the water, producing high-purity soft water with almost no impurities. It is particularly suitable for high-end industrial fields with extremely strict water quality requirements, such as ultrapure water preparation, high-end electronic equipment cleaning, etc. In addition, the reverse osmosis method has a high degree of automation, stable operation, and small footprint. However, the reverse osmosis method also has some shortcomings. It has high requirements for the water quality of the incoming water, and requires strict pretreatment of the raw water to prevent the semipermeable membrane from being contaminated and blocked. Moreover, the investment cost of the reverse osmosis equipment is high, and a large amount of electricity is consumed during operation, resulting in relatively high operating costs.
6. The health code between hard and soft water
Hard water and soft water are not only very different in industrial production, but also have their own unique effects on human health. Understanding these effects can enable us to make more scientific drinking water choices in daily life.
Let's talk about hard water first. It is rich in minerals such as calcium and magnesium. Drinking hard water in moderation can actually supplement the calcium and magnesium ions needed by the human body. Calcium is an important element for maintaining bone and tooth health. Adequate calcium intake helps prevent osteoporosis. Magnesium participates in many physiological processes of the human body, such as regulating heart rhythm, maintaining nerve and muscle function, etc. Studies have shown that the incidence of cardiovascular disease in areas where hard water is consumed for a long time is relatively low, which may be related to the protective effect of magnesium in hard water on the cardiovascular system. However, hard water is not without disadvantages. When the hardness of hard water exceeds a certain limit, long-term drinking may increase the risk of diseases such as kidney stones and gallstones. This is because excessive calcium and magnesium ions in hard water may combine with other substances in the human urinary system to form insoluble stones. In addition, hard water may not be very friendly to people with weak gastrointestinal function, and it is easy to cause gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating and diarrhea. Let's take a look at soft water. Due to its low content of calcium and magnesium compounds, drinking soft water in moderation can reduce the risk of calcium stones to a certain extent. Moreover, soft water usually tastes better, has lower bacterial content after boiling, and is more refreshing to drink.
There are also some potential risks in long-term reliance on soft water. Soft water has a low mineral content. If you drink it for a long time, it may lead to human mineral deficiency, especially insufficient intake of important elements such as calcium and magnesium. This may affect the health of children, pregnant women, the elderly and other people who have a high demand for minerals.
For example, long-term drinking of soft water by children may affect the normal development of bones; the elderly may increase the risk of osteoporosis. In addition, studies have shown that long-term drinking of soft water may also reduce the activity of various enzymes in the body, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. So, what is the range of water hardness suitable for drinking? According to the latest GB 5749-2022 "Sanitary Standards for Drinking Water", the total hardness of drinking water (calculated as calcium carbonate) shall not exceed 450mg/L. The World Health Organization believes that the hardness of drinking water is most suitable at around 170mg/L. Within this range, it can not only ensure that the human body obtains certain minerals from water, but also reduce the health risks caused by excessive hardness. Of course, this is only a rough reference range. For individuals, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as their own health status and eating habits. For example, for people who already suffer from stone disease, it may be more suitable to drink water with lower hardness; while for people who do not take in enough calcium and magnesium in their diet, drinking water with slightly higher hardness may be beneficial. In daily life, there are still some common health misunderstandings about hard water and soft water. Some people think that as long as hard water is boiled, the harm of hard water can be completely eliminated and it can be drunk with confidence. Although boiling can make some calcium and magnesium ions in hard water form scale and precipitate, reducing the hardness of water, it cannot completely remove all calcium and magnesium ions. For hard water with higher hardness, even after boiling, its hardness may still exceed the range suitable for drinking. Some people think that soft water is healthier than hard water and should only be drunk. As mentioned earlier, long-term drinking of soft water may lead to mineral deficiency and have adverse effects on health. In fact, whether it is hard water or soft water, the key lies in moderation and balance. We should choose drinking water reasonably according to our actual situation, and pay attention to supplementing the minerals that may be lacking through other foods.


629.webp)



294.webp)
476.webp)
420.webp)
146.webp)
460.webp)
287.webp)
274.webp)
688.webp)


